Hydrogen
Lightweight, Simple and Fast Solution for Charged Up.
Team Lead & Lead Programmer
January 2023 - April 2023
IronPulse Robotics - Shanghai Pinghe School
Project Robot Java Control Theory Path Planning
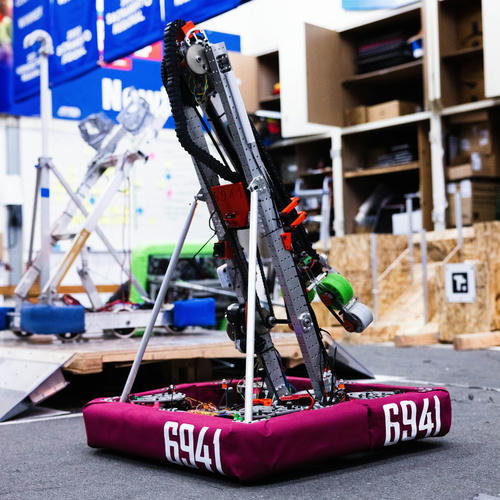

Hydrogen is the robot I programmed and assembled for FIRST Robotics Competition 2022. It has some exploration in the field of real-time path planning, autonomous navigation, and residual tag identification. Hydrogen participated at Sacramento Regional in year 2023.
Hydrogen is the third robot I programmed for FIRST Robotics Competition (FRC) Season 2023 - Charged Up. It is the second robot I've programmed.
Hydrogen is designed to be fast, agile, and simple on the field. The only actuation mechanism for Hydrogen is a RP manipulator - one degree of revolution plus one degree of prismatic action. This allows us to reach all the scoring level while making the robot as simple as possible.
Innovations
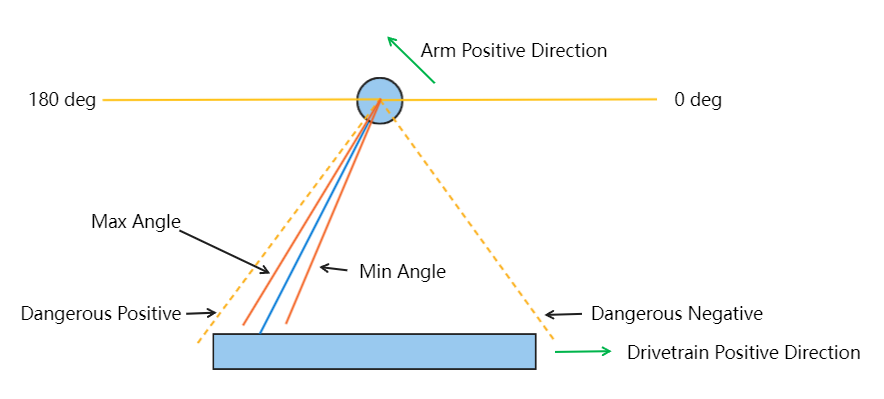
Superstructure Kinematics
The whole superstructure is fully described using RP manipulator kinematics. As it only has 2 degrees of freedom, it is easy to describe using trigonometric functions. Using this, we are able to plan the movement of the robotics arm, preventing it from entering dangerous zones (e.g. hitting the ground when over-extending), while compensating gravity based on the current angle of the arm.
Custom April Tag Localization
For accurate position estimation, we reused the Kalman Filter in Acetate for pose estimation. Now, localization is more accurate as the robot can receive updates from residual vision targets, allowing error to be controlled at centimeter level in close range.
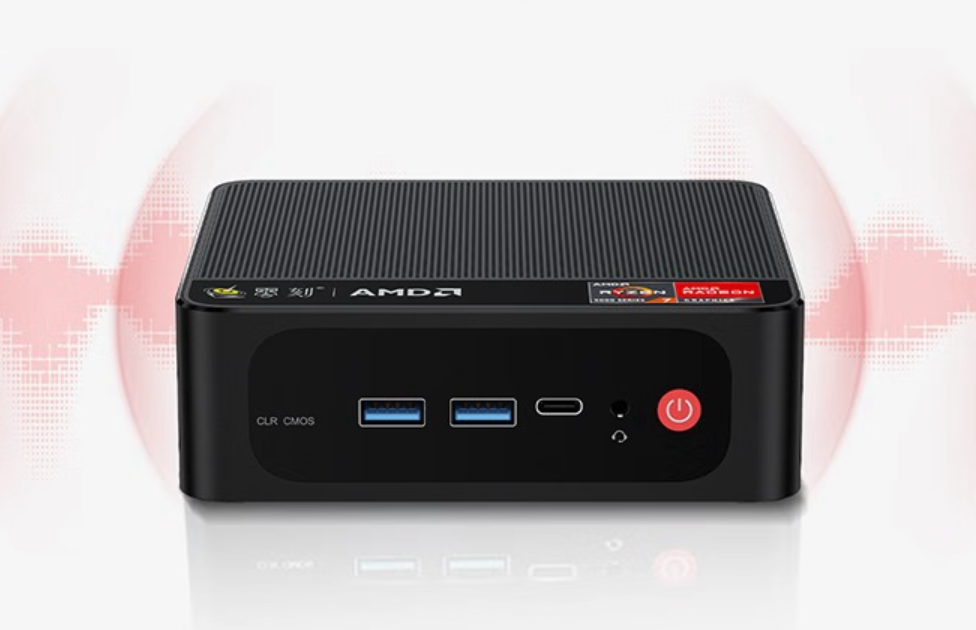
Due to the real-time requirement of the competition, we decided to build a custom onboard computing system to rapidly detect and calculate the translation of April Tags. The system consists of a 5800H mini-pc, powered in 19v after buck-boost. For stability of power, we also used capacitors to reduce the fluctuation in voltage supply due to the action of our robot.

A* Path Planning
The game is mainly a large, flat field, allowing space for high-speed actions and collisions. However, the existence of charging stations becomes an obstacle on the direct way to the scoring spot. To overcome the potential instability of human drivers and operators, while having the support from April Tag information and localization based on Kalman Filters, we decided to use path-finding algorithms, namely A*.
Our path-finding algorithms divide the map into small grids and explore in 8 directions. During the exploration, there's an adjustable heuristic value h for a tradeoff between accuracy and speed of exploration. We also provided a class to define "obstacles" on the way to the target, and the path planning algorithm will mark those points as invalid when it goes into that region. After finding the path, the algorithm will carry out Floyd Trimming to reduce the number of path points, finally sending back the path to the action command. The action command will "look ahead" by a certain distance on the path, and the drivetrain will follow the path using a PIDF controller at the very end.
The whole path-planning algorithm is asynchronous. After sending the command, the operator can still carry out movement while waiting for another thread to finish path planning. But as the planning process usually takes less than 0.2 seconds, this function is not usually felt.
Operator Web Interface
As Charged Up has 27 (9 * 3) targets on the grid in total, it becomes complicated for the operator to select the target. For better and more intuitive target selection, we developed a web interface system, allowing the operator to interactively choose the target scoring grid, scoring column, and scoring row. The system will also update the status of the robot while allowing the configuration of some of the parameters.
Auto
With the support of "Codeless" Autonomous, the development of autos becomes easier this year. We are able to build 5 sets of autonomous routines for different sides of the fields we are on. At the same time, for the special "balancing" mission at the end of the autonomous period, we programmed a special movement based on the reading of the gyro and the drivetrain encoders.
COG & Stability
One of the biggest weaknesses of Hydrogen is that it has a very high COG. The lightweight drivetrain is prone to tipping when the robot fully extends its manipulator for placing pieces, causing it to overturn. When going over the field, the robot may even turn over during high-speed collisions with the opponents. This led to the failure of the robot at the competition.
Development Story
Hydrogen is mainly built during the winter vacation of year 2023. During restrictions of the COVID pandemics, we still have to move out